Mitosis
Friday, March 2, 2012
What is the biological purpose?
The main purpose of mitosis is for growth and repair of cells. In order for our bodies to grow we must go through cell division. Our bodies undergo mitosis in order to fix breaks and cut my reprodcuing more cells to repair the damage. The biological purpose is to give all eukaryotic cells the ability to reproduce with out sperm and egg.
What are the key events?
Prophase: the nucleus dissolves, chromatin are condensed into chromosomes, centrioles begin moving to opposite sides of the cell and fibers extend from the centromeres
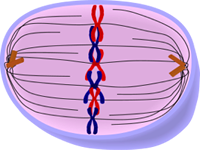
Metaphase: spindle fibers align chromosomes in the middle of the cell referred to as the metaphase plate. This helps to ensure that each new daughter cell will receive on copy of each chromosome.
Anaphase: the chromosomes are pulled apart by centrioles
Telephase: chromatids arrive at opposite ends of the cell and new membranes are formed around the daughter nuclei
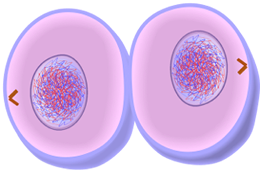
Cytokenisis: the cytoplasm divides and two new daughter cells are formed
What is the outcome?

The outcome of mitosis is two identical nuclei identical the parent nucleus. It is usually followed by cyokinesis resulting in two identical cells.
what is mitosis?
Mitosis only occurs in body cells and it produces two genetically identical cells by replicating itself. Mitosis occurs after the G2 phase. In all, there are six phases of mitosis. They are interphase, prophase, metaphase, teleophase and cytokenisis. In the process of mitosis, ONLY the nucleus and the nuclear material is what is being divided. This happens because the DNA replicates from the parent cell to create 2 daughter cells. During mitosis, the cell duplicates all of its contents and splits to form the two new daughter cells in a very complex process of steps. These steps are controlled by genes, and when not followed through properly, cancer and other health problems can occur.
What are the phases of mitosis?
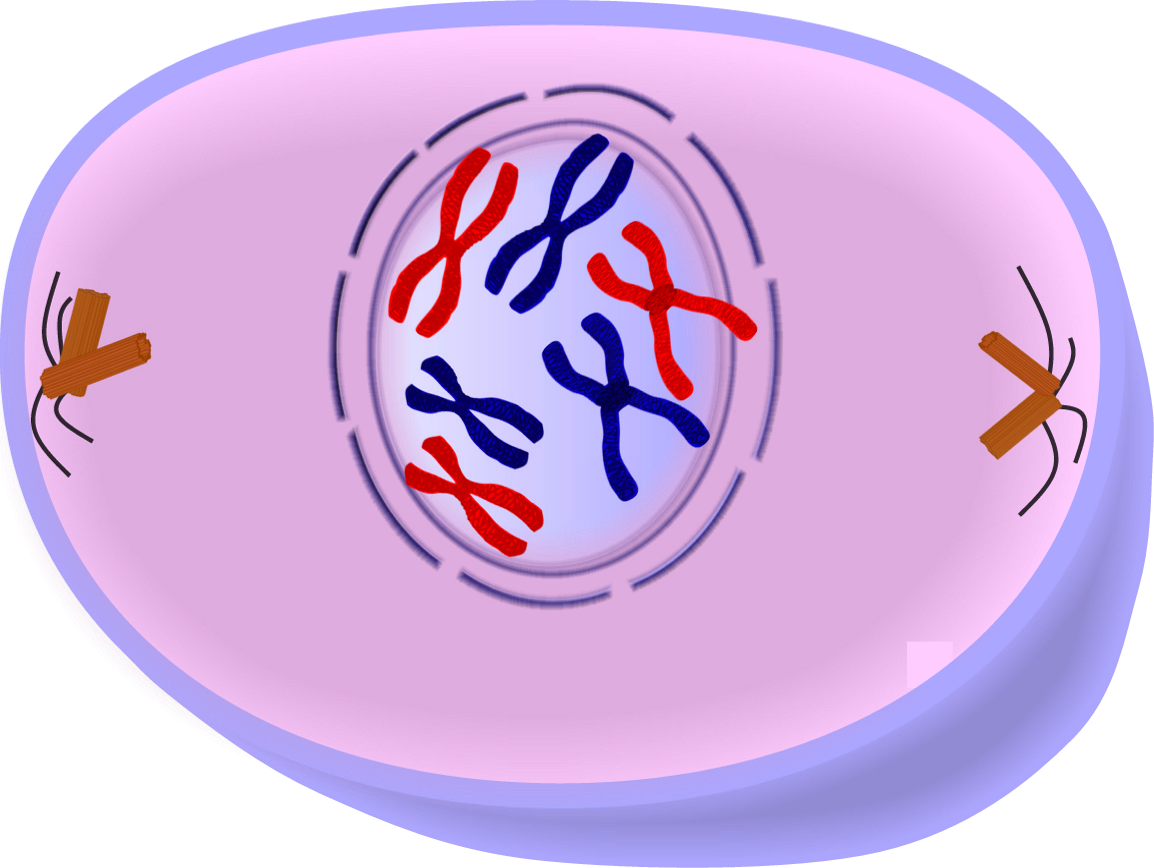
The first phase of mitosis in interphase. Interphase proceeds in 3 stages. Growth 1, synthesis and growth 2. Interphase is a phase of the cell cycle, defined by the absence of cell division. During interphase the cell obtains nutrients, and duplicates its DNA. Throughout the G1 phase of interphase is when the cell grows and replicates its organelles. During Synthesis, the cell synthesizes its DNA. Lastly, during G2 the chromosomes begin to condense and assembly of the spindle begins.
_3D.png)
The second phase of mitosis is Prophase. This is the preparation phase for the cell. The nucleus dissolves and the chromatin condenses into chromosomes.
The third phase of mitosis is metaphase. During this phase, the chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell to prepare to be pulled apart during anaphase.
The fourth phase of mitosis is anaphase. During this phase the chromosomes are pulled apart by the centrioles.
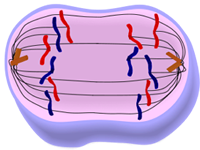
The fifth phase of mitosis is telophase. throughout this phase the cells nucleus reforms.
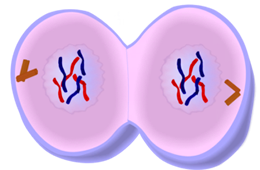
The sixth and final phase of mitosis is cytokinesis. This is when the cytoplasm divides and the cell splits into two.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)